Pat, OzzyDog - thank you for watching this thread!
____________________________________________________
Actually I am preparing data from the original Douglas blueprints to verify my model. For the beginning I chosen the wing. This is a well-documented assembly, because I found a master diagram in the NASM microfilm that describes SBD wing geometry (ordinals). Below you can see the first sheet of this diagram (dwg no 5090185):
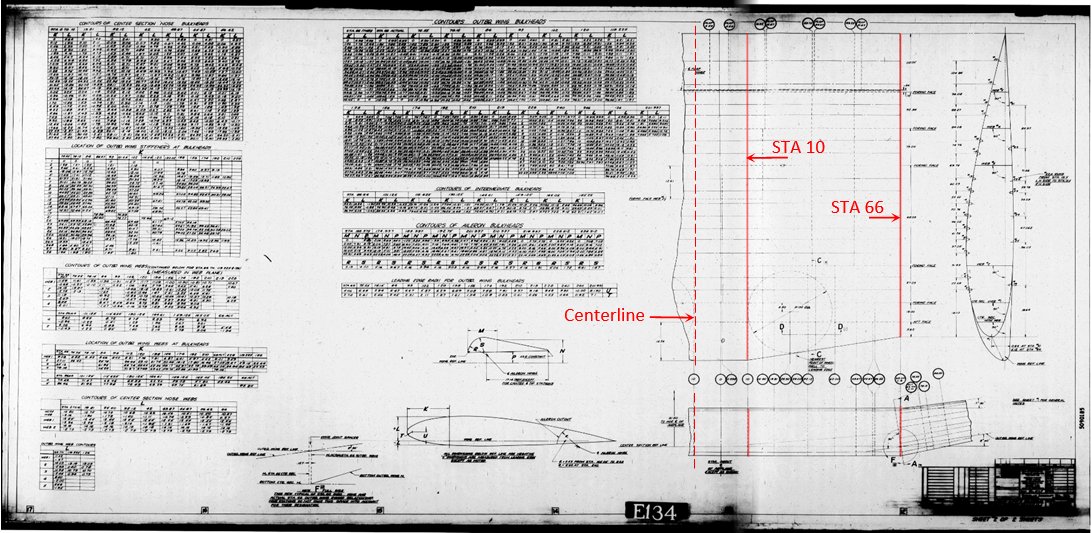
Here you can download its high-resolution version (5MB). As you can see, it contains the ordinal tables of the wing bulkheads (ribs) and webs (spars). In the sketch on its right side Douglas engineers depicted various other dimensions of the wing center section. In the picture above I marked in red its key wing stations. Their names correspond to spanwise distance in inches from the aircraft centerline: “STA 10” is 10” from the centerline, while “STA 66” is 66” from the centerline.
Another part of this diagram contains a sketch of the larger, outboard wing section:
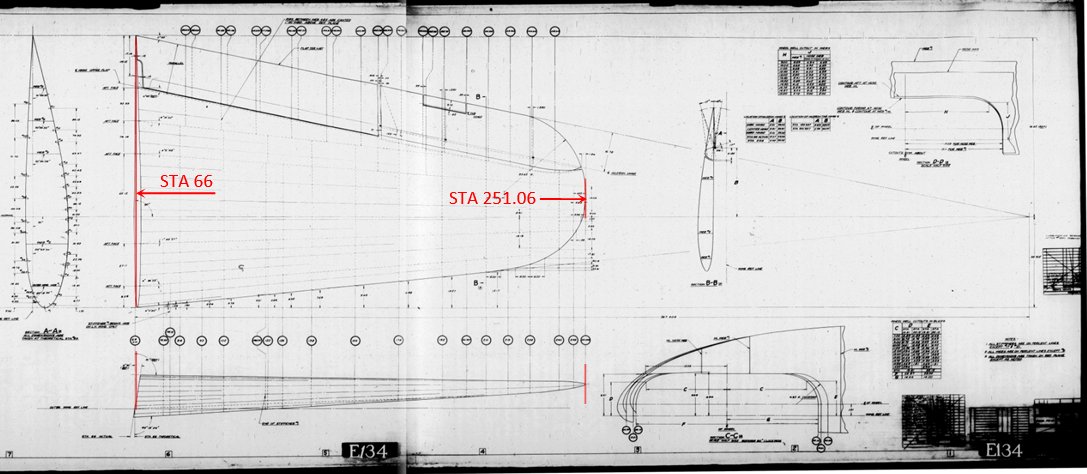
Here you can download its high-resolution version (7MB).
Wing station names of the outboard section starts with “STA 66” and continue to the tip, which is named “STA 251.06”. This distance – 251.06” – is measured spanwise, along the reference planes of the outboard and center wing sections.
The first thing that I noticed comparing these blueprints to my model, are the different reference planes:
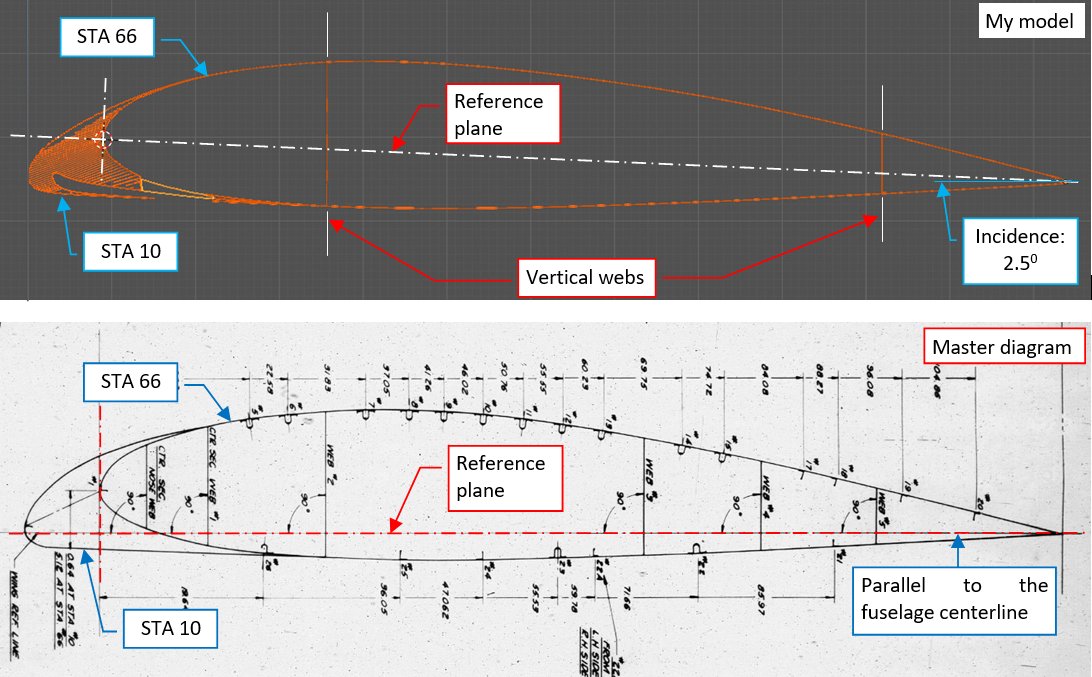
For my model I chosen the airfoil chord as the reference plane, with the origin point at the tip of the airfoil nose. (Airfoil coordinates are specified in such a reference system). The SBD wing was inclined at 2.5°, thus I rotated my wing object by the corresponding angle. However, from the photos I learned that SBD webs (spar) planes were vertical, so I adjusted their directions in my model. (If they were also inclined at 2.5°, connecting webs to the fuselage bulkheads would be much more complex, i.e. heavyweight).
In the original Douglas diagram shown above you can see that its engineers took different approach: they used re-calculated airfoil ordinals for given inclination angle. In this way their reference plane crosses the wing trailing edge and remains parallel to the fuselage centerline and perpendicular to the web planes. It seems that it was a standard approach in that era: I have found similar solution in the original Curtiss P-40 blueprints.
Building my model, I used simplified stations diagram from the SBD Maintenance Manual. From that diagram I knew that the wing tip station was at 251.06”. I also correctly assumed that the station distances are measured along the corresponding reference planes of the center and outboard wing sections.
In principle I was right, but I assumed wrong reference plane for the outboard wing! Below you can see the plane that I assumed for my model, and the real reference plane from the Douglas master diagram:
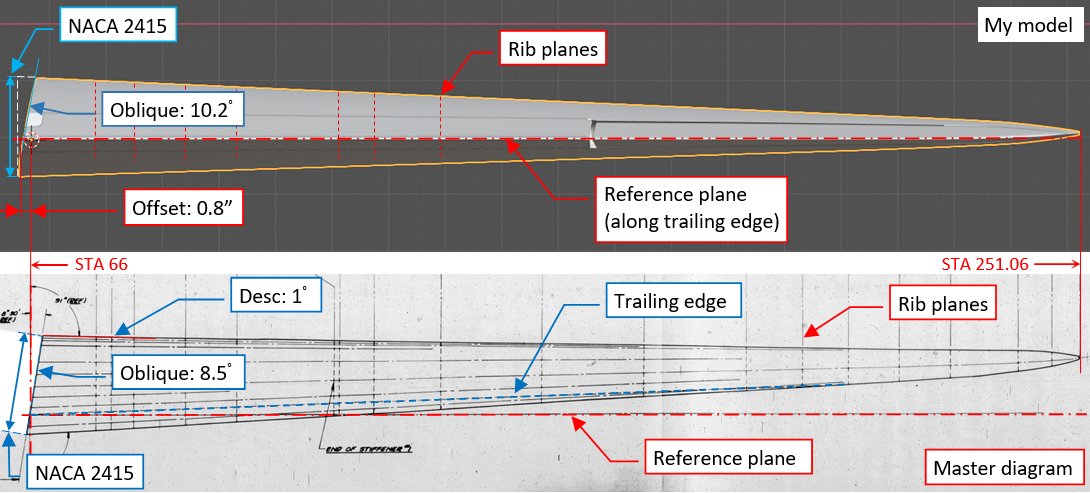
Usually designers choose reference planes along an easily distinguishable element, which you can use as the base for physical measurements. Their choice is extremely important for the technology used in the manufacturing (i.e. ultimate product cost), because these reference bases are reflected in the tooling geometry. In the case of the aircraft wing the most obvious candidate for such a base is the trailing edge. However, in this wing Douglas engineers chose a strange reference plane, which fits to nothing! Look at the fragment of Douglas master diagram above: every spanwise line of the wing is oblique: trailing edge, leading edge, upper wing contour (1° downward), lower wing contour… It does not even fit any spanwise contours of its webs (all of them are trapezoids). There was no chance to discover such a thing without this master diagram blueprint!
However, I knew that there is something wrong with the geometry of my wing. To obtain the dihedral angle specified in the SBD Maintenance Manual (in the front view: 7.5° along the wing upper contour) in my model I had to raise the outer wing section by 10.2°. For such an angle, I obtained wing span of 496.4”, which is 1.73” short of the documented value. I checked again station locations, to make sure that I did not made an error. I found nothing wrong, thus all what I could do was just to compensate this difference by additional 0.86” offset to each wing. (In picture above I marked it at station 66). Now it is clear, that this difference was caused by the wrong choice of the reference plane. In the master diagram this wing is already “pre-rotated”, and you have to raise it by only 8.5° to obtain the proper dihedral angle.
I also made another error. Building the wing model I assumed that declared, 15% thick airfoil NACA2415 at station 66 (joint of the center and outboard wing section) was perpendicular to the reference plane of the outboard wing (i.e. to the wing airfoils chords plane – see figure above). In the effect, I obtained the oblique rib (10.2°), adjacent to the wing center section, as 15.24% thick. Now from the STA 66 ordinals of I learned that they used the 15% NACA2415 for the oblique rib, thus the real wing was somewhat thinner than in my model.
I recreated the ordinals from the master diagram as polygons in 3D space of my model. These are all five webs and some key ribs. You can see their arrangement in figure below:
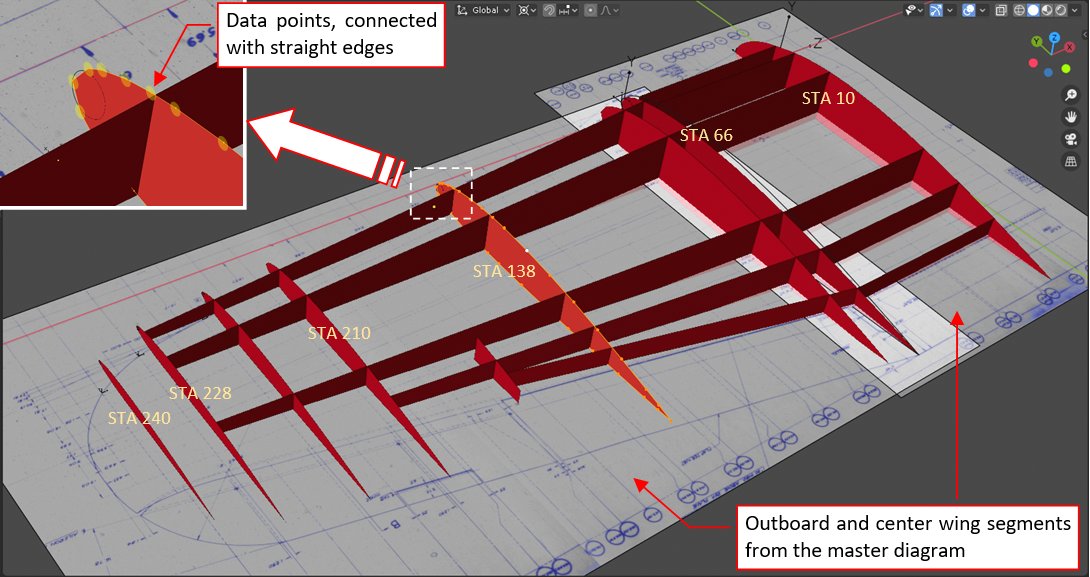
In the picture above the ribs seem to be smooth, but look at the enlarged nose of STA 138: their vertices (ordinals) are connected with straight edges.
Note also see fragments of the master diagram image placed on the reference plane. To easily place rib polygons at their stations, I used single reference plane for both wing sections (i.e. the outer wing has no 8.5° dihedral). Thus at this moment the outer section is minimally raised above the reference plane, as it was according the ordinals. You can see this arrangement better in the picture below, taken from another viewpoint:
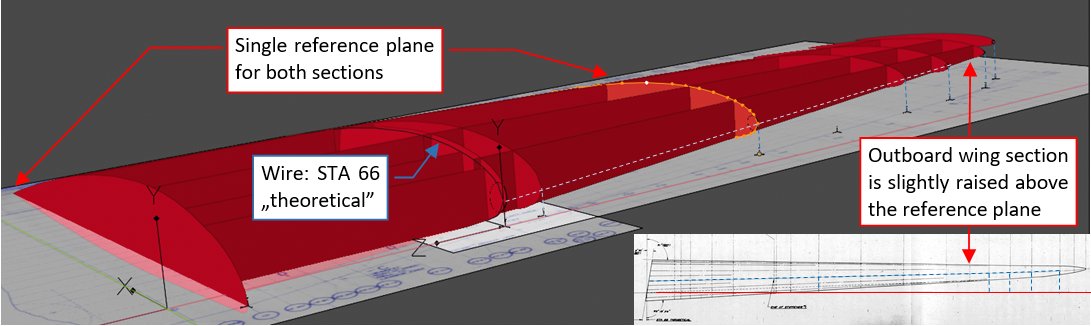
For the outer wing section I also recreated the ordinals of theoretical (i.e. in this arrangement - vertical) STA 66 contour. However, this is just a wire (a “theoretical entity”) – because the real rib at outer STA 66 was oblique.
Figure below shows the wing tip contour geometry specified in the master diagram:
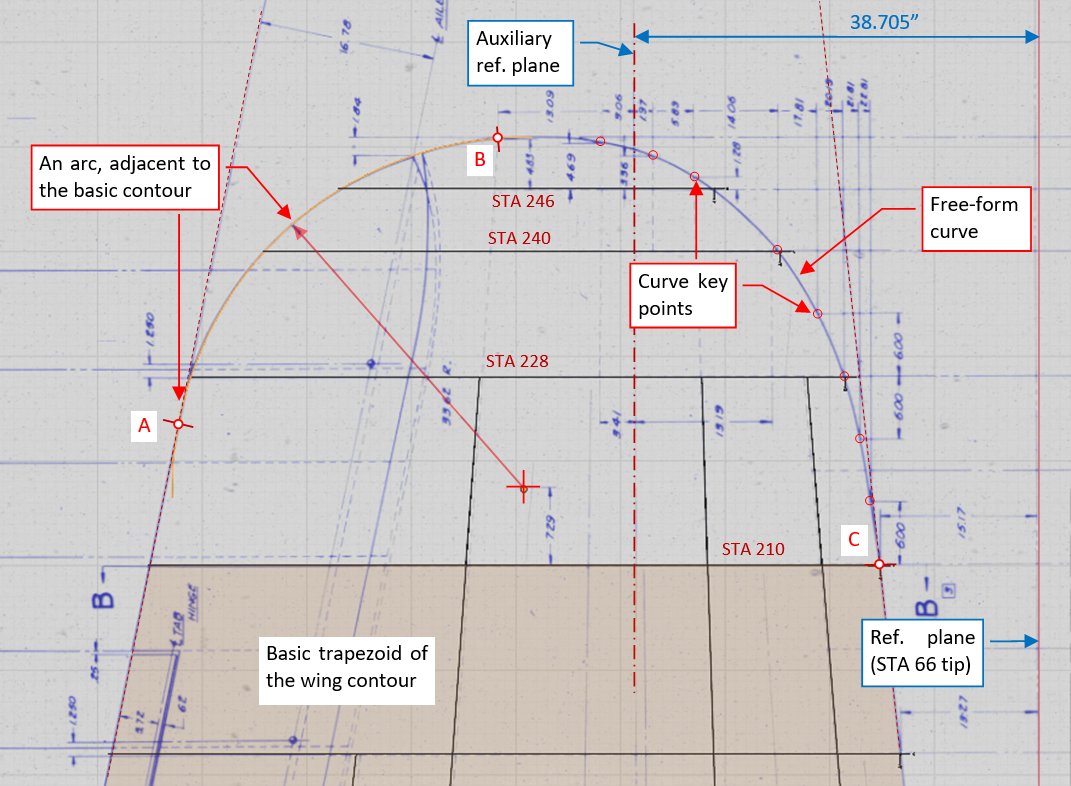
The rear part of this contour (from point A to B) is shaped by an arc, which radius is 33.62”. The forward part (from B to C) is a free-form curve, described by a few key points, dimensioned in this drawing.
In this drawing you can see an auxiliary reference base, placed at 38.705” from the basic reference plane (located at STA 66 nose tip). This additional reference was introduced to facilitate dimensioning various wing tip details. The master diagram describes this line as “common percent line”, perpendicular to aircraft centerline. In trapezoidal part of the wing it connects points located at 33% of their airfoil chord lengths.
For initial verification of wing tip contour, I also placed over this fragment the assembly drawing of the wing tip. You can see the result below (lines from the master diagram are blue, from the assembly drawing – black):
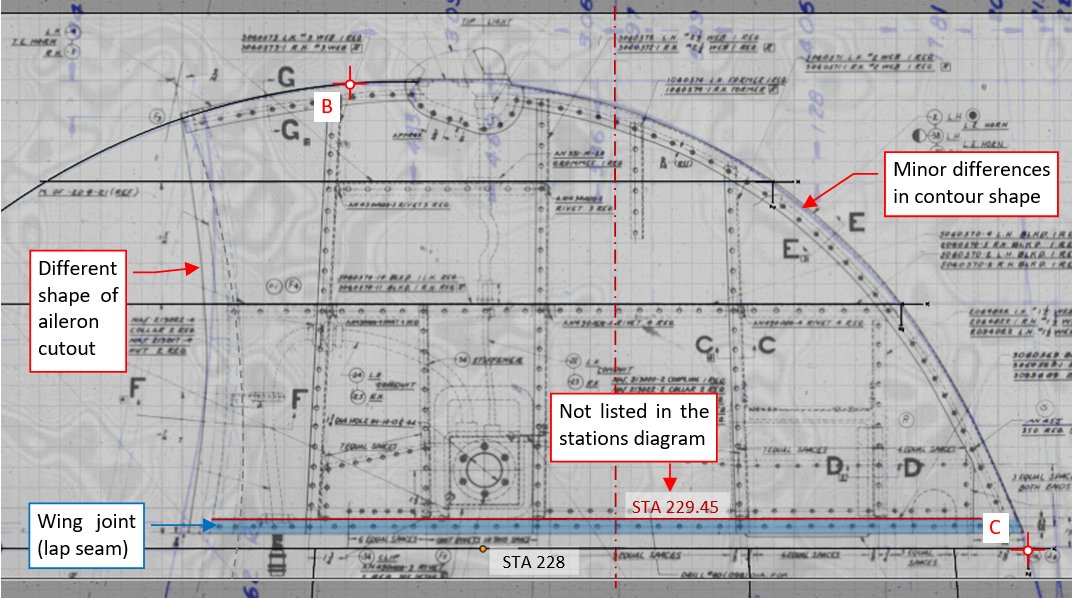
In general, both contours match each other, within the tolerance of the manual sketching and eventual later deformations caused by microfilm camera lenses. However, the shape of aileron cutout significantly differs between these two drawings. What is interesting, photos of the restored SBDs confirm the variant depicted in the assembly drawing.
The width and height of the basic grid “square”, visible in this and further pictures in this post, correspond to 1 in.
In this assembly drawing I also identified additional rib (bulkhead) at STA 229.45. It did not occur on the stations diagram. However, the SBD wing tips were demountable, so its presence just at the joint seam is quite obvious. (The rib at STA 228 was its counterpart from the other side of this seam).
I placed on this drawing the free-form curve key points, following the explicit dimensions specified in the master diagram, and connected them with a curve. I was surprised, discovering that the central part of this contour does not fit both drawings:
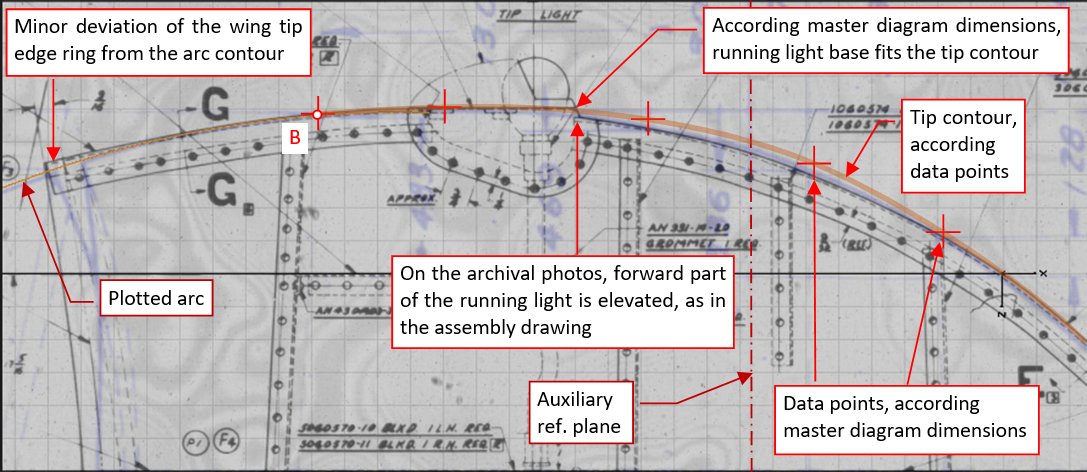
The difference between these contours is quite significant and reaches about 0.4” near the auxiliary reference plane. All what I could do in such a case was checking this detail in the available photos (especially the archival photos). Unfortunately, it is impossible to precisely compare this shape with the perspective images of real wings. That’s why I focused on the contour of the running light base. In the assembly drawing its forward part elevates a little above the win tip contour, while according the master diagram curve there would be no such elevation. I can say that you can observe such an elevation in most of the restored aircraft and in all of the archival photos. They confirm the wing tip shape depicted in the assembly blueprint.
The same applies to the small deviation from the master diagram contour at the aileron tip. It would be difficult to bend the end of the tip edge ring precisely around the master diagram “mathematical” arc contour, because of the sudden change in the curve radius at point B. (In that era aircraft designers cared only about the tangent continuity of their theoretical contours).
What’s more, the master diagram does not specify many other wing tip geometry details, for example – it misses the cross-section radius of the wing tip edge ring. To determine it, I had to use the detailed drawings of the wing tip webs. Ultimately I verified the wing tip shape using all available images of its parts:
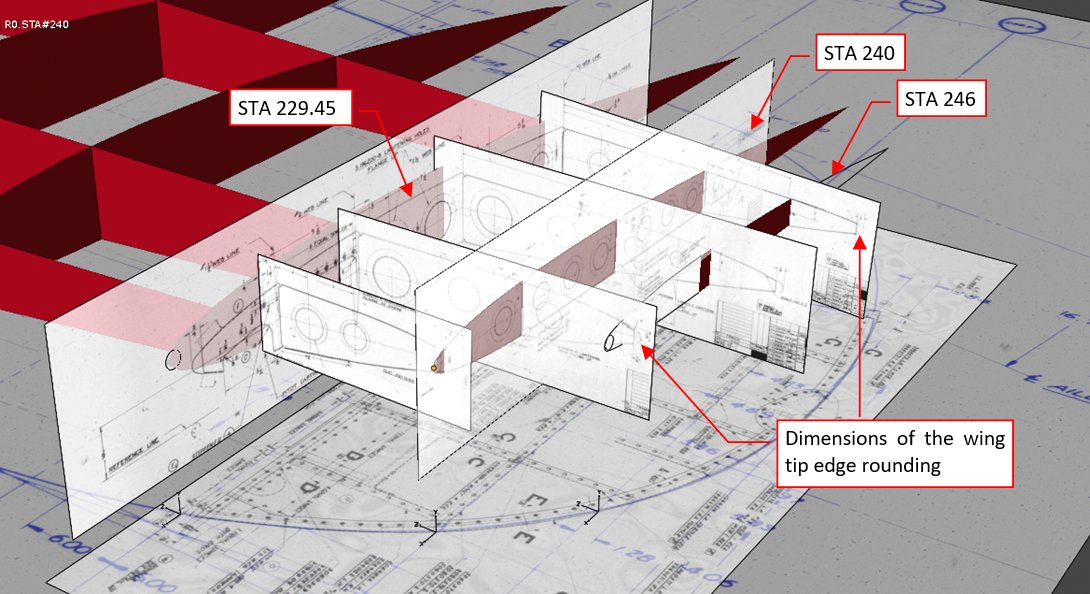
I have found some further differences between the wing tip webs and ordinals of STA 246. (This is the last wing station, specified in the master diagram. Most of its shape is purely theoretical, because only its central part corresponds to a real partial rib).
I also found some other, less significant differences in the center wing section (for example – in the middle of STA 10).
Finally I concluded that the master diagram describes an initial concept of the wing shape, which was later (in the prototype workshop?) slightly modified, especially at the wing tip. Thus in all these cases I decided to rely on the assembly drawings.
Below you can see the complete “reference structure” which I prepared for the SBD wing:
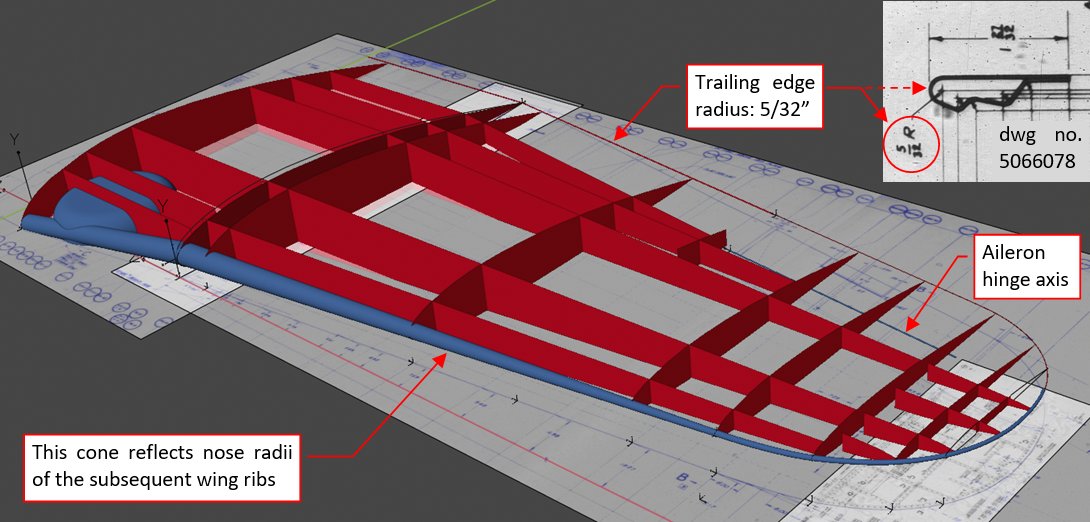
Around the leading edge I placed a long, bent cone, which reflects its varying radius. Similarly, I signalized the radius of the trailing edge by marking it with two thin “tubes”. According the flap assembly drawing (dwg. no. 5066078) the outer radius of the flaps trailing edge cross-section was 5/32” (which means that they were about 0.3” thick). Aileron trailing edge was somewhat thinner: according the master diagram and assembly drawing the radius of its inner wedge was 0.09”. Because the SBD ordinals do not include the eventual skin thickness, I had to assume that sheet metal used as the overlay in the aileron structure was 0.05” thick. In the result I obtained the ultimate thickness of aileron trailing edge as 0.28” (2*0.09 + 2*0.05). I also added other details, as the landing gear wheel bay and aileron hinges axis (both dimensioned in the master diagram).
Before matching my model to this “3D reference frame”, I decided to check at least one of its overall dimensions – just in case. The most obvious candidate was the wing span, which I could read from the general arrangement drawing: 41’ 6⅛”:
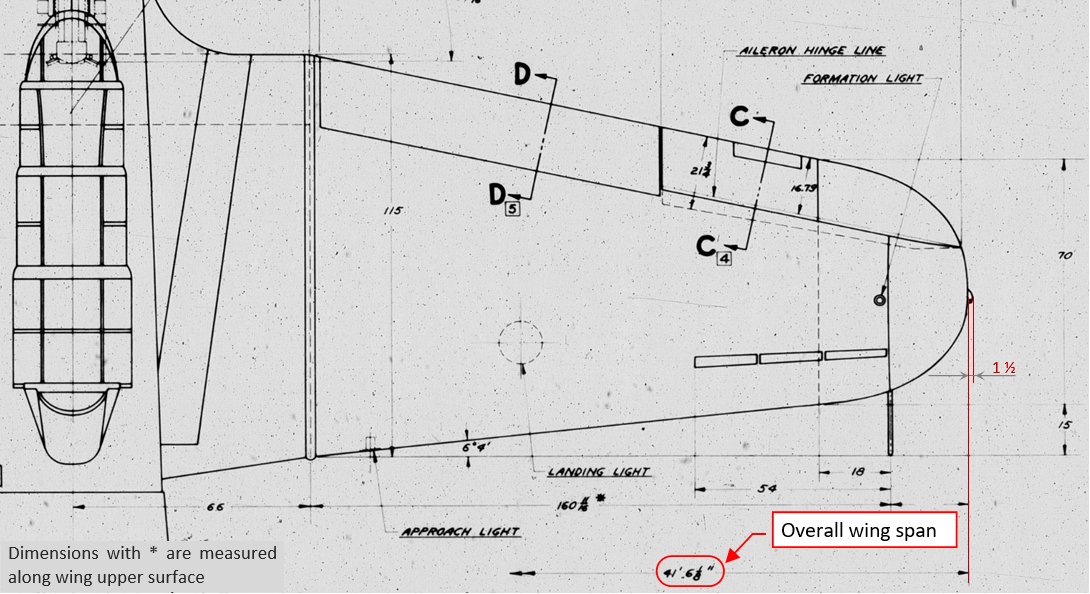
Note that it was measured precisely between the tips of the curved wing contour: the widths of the running lights (1.5” for each side) were not included. (The width of these running lights was specified in the front view of this drawing). I also noted that the SBD maintenance manual specifies slightly different wing span: 41’ 6.3”. More precisely: according dwg 5120284 the distance from the center plane to the wing tip was 498.125”/2 = 249.063”, while the maintenance manual shows it as 249.187”. The difference: 0.124” on each side of the aircraft was minimal, but this wing was identical in all Dauntless versions. Which of these dimensions is wrong?
I made a quick calculation using the stations diagram: if the distance to the wing tip measured along the reference planes was 251.06”, then the half of the wing span is: 66 + (251.06-66)*cos(8.5°):
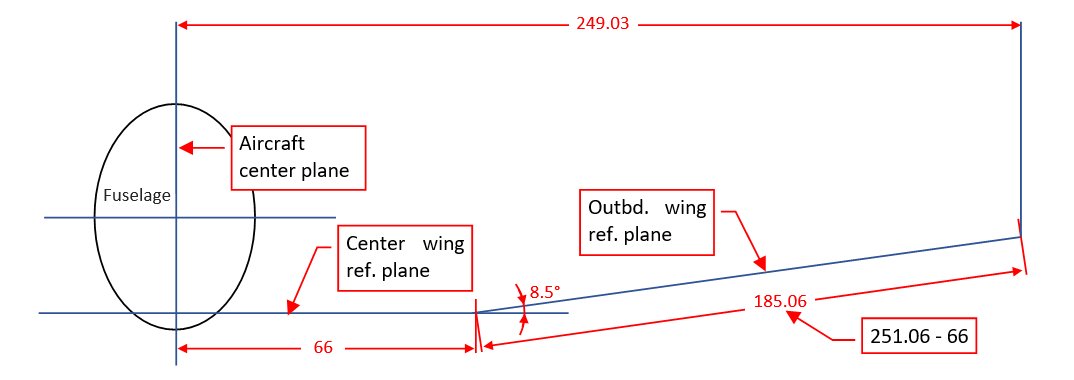
The result is 249.03”. However, the SBD ordinals describe “skeleton geometry” and did not take into account the skin thickness. Thus I have to add to this result the typical thickness of the wing skin: 0.03”. Finally it gives distance of 249.06”, which perfectly agrees with arrangement drawing 5120284.
Reassured by these calculations, I raised the object representing the outboard wing in my 3D “reference frame” by 8.5°, and measured the distance from its tip to the center plane. I was really surprised by the result:
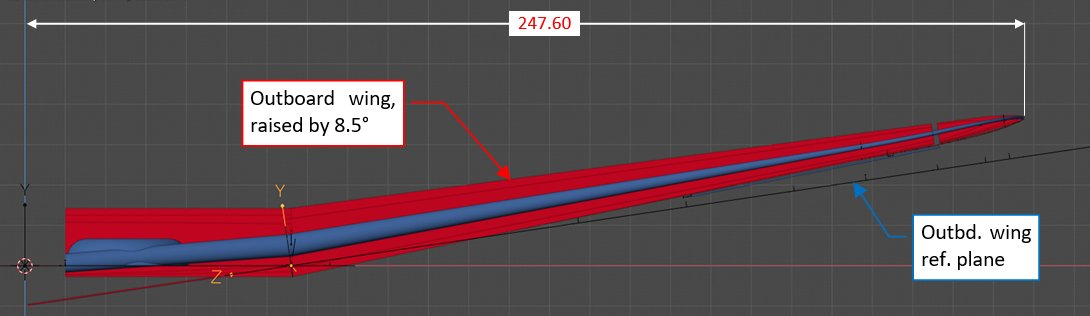
Well, the reason for obtained dimension – 247.60”, instead of 249.03” – is simple: in my calculations I did not take into account the initial elevation of the wing tip over its reference plane:

In the result of the rotation by 8.5°, the wing tip is 1.43” closer to the aircraft center than STA 251.06, placed on the reference plane.
As you can see, the location of the of the SBD outboard wing reference plane is so unusual that even Douglas engineer, who provided dimensions for the arrangement drawing, made the same error as mine.
Thus the true wing span of the Douglas SBD was:
- 41’ 3.2” between the wing tips (i.e. between bases of the running lights);
- 41’ 6.2” between tips of the running lights;
Note that without the arrangement drawings you can easily make another error, and compare the wing span provided in the most of publications (41’ 7”) with the distance between the tips of the running lights. The result you will obtain in such a case will be quite close to the real value, because these two errors compensate each other.
Wing span from the SBD maintenance manual (41’ 6.37”) is also wrong. Was this slightly higher value (249.187” instead of 249.063” from dwg 5120284) obtained by adding the sheet metal thickness of the tip lights bases?
On the other hand, in the practice the precise overall wing span was seldom or never used. During production, the most important thing was the proper fitting of the wing segments at STA 66, and compliance of the basic assemblies to their own overall dimensions. To fit an aircraft in a hangar, you always have to provide an additional space of at least few inches on each side. During the operational use of these SBDs, board crews probably did not even notice that they occupied minimally less space than specified. For the long-term stowage or the transport the outboard wing sections were detached, and in this case the overall aircraft dimensions precisely matched the documentation. It seems that the aircraft length and span are most useful for the modelers, who use them for checking their scale plans or model kits.
However, this is one of the most unexpected errors that I encountered so far. Previously I have identified significant wing span mistake in the case of the Fokker D.V drawings from 1916, but I thought that such a thing could only happen in the era of the sketches made with chalk on the workshop floor. I would never expect such a mistake in a dimension from the original blueprints made in 1940!